Example #1:
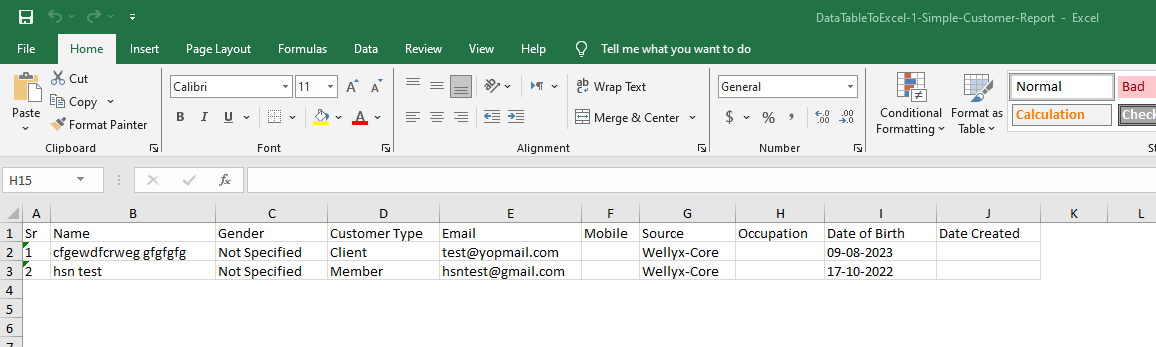
The below given C# code snippet demonstrates how to use the ExcelBuilder utility to create a Simple Excel file with a table. Here's a bit of description:
// Create a new instance of ExcelTable
ExcelTable simpleexcelTable = new ExcelTable();
// Add header and data rows to the table
simpleexcelTable.Rows.Add("Sr", "Name", "Gender", "Customer Type", "Email", "Mobile", "Source", "Occupation", "Date of Birth", "Date Created");
simpleexcelTable.Rows.Add("1", "cfgewdfcrweg gfgfgfg", "Not Specified", "Client", "test@yopmail.com", "", "Wellyx-Core", "", "09-08-2023", "");
simpleexcelTable.Rows.Add("2", "hsn test", "Not Specified", "Member", "hsntest@gmail.com", "", "Wellyx-Core", "", "17-10-2022", "");
// Build the Excel file using ExcelBuilder
using (var excelBuilder = ExcelBuilder.Datasets(simpleexcelTable).Build())
{
// Specify the file path where you want to save the Excel file
string filePath = "DataTableToExcel-1-Simple-Customer-Report.xlsx";
// Save the Excel file
excelBuilder.SaveAsFile(filePath);
}
This code creates an Excel table with header and data rows and saves it to a file named "DataTableToExcel-1-Simple-Customer-Report.xlsx". The ExcelBuilder utility simplifies the process of creating Excel sheets, making it easy to generate structured reports.
Example #2:
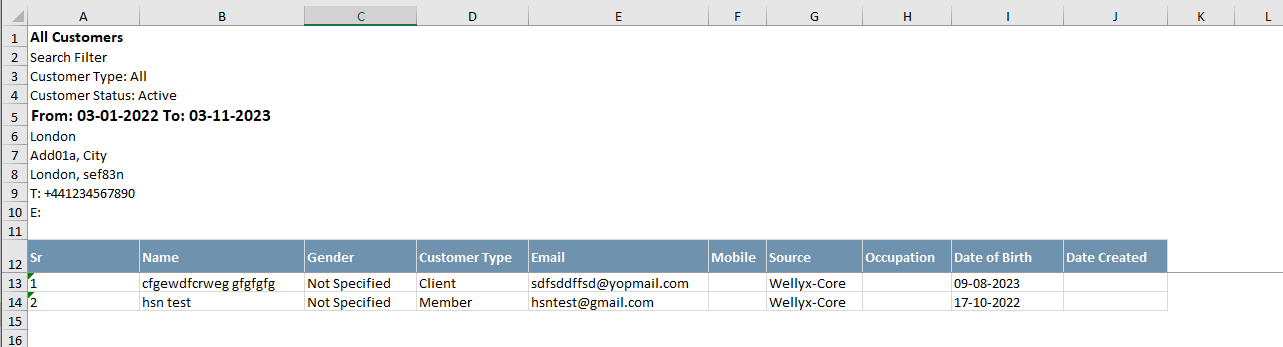
// Create an instance of ExcelTable to structure and organize data for Excel sheet
ExcelTable excelTable = new ExcelTable();
// Populate the Excel table with rows containing filter information and customer details
excelTable.Rows.Add(new ExcelRow(new RowStyle(false) { FontBold = true, FontSize = 12 }, "All Customers"));
excelTable.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false), "Search Filter").SpanToMaxRowCells();
excelTable.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false), "Customer Type: All").SpanToMaxRowCells();
excelTable.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false), "Customer Status: Active").SpanToMaxRowCells();
excelTable.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false) { FontBold = true, FontSize = 13 }, "From: 03-01-2022 To: 03-11-2023").SpanToMaxRowCells();
excelTable.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false), "London").SpanToMaxRowCells();
excelTable.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false), "Add01a, City").SpanToMaxRowCells();
excelTable.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false), "London, sef83n").SpanToMaxRowCells();
excelTable.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false), "T: +441234567890").SpanToMaxRowCells();
excelTable.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false), "E: ").SpanToMaxRowCells();
// Add an empty row to separate filter information from customer details
// The `SpanToMaxRowCells` method is used to span a row's content across all available cells in a row.
// This is particularly useful for creating header or filter rows where a single piece of information
// should cover the entire width of the Excel table, regardless of the number of columns.
// In the provided code snippet, `SpanToMaxRowCells` is applied to certain rows, ensuring that specific
// filter information, such as "Search Filter," "Customer Type: All," etc., spans across all columns.
// This method enhances the visual representation of filter-related details, making them stand out and
// improving the overall structure and readability of the Excel sheet.
excelTable.Rows.Add().SpanToMaxRowCells();
// Add header row with styling for customer details
excelTable.Rows.Add(new RowStyle
{
FontBold = true,
Height = 25,
AlignmentVertical = XLAlignmentVerticalValues.Center,
BackroundColor = XLColor.FromHtml("#6F93AE"),
FontColor = XLColor.White
}, "Sr", "Name", "Gender", "Customer Type", "Email", "Mobile", "Source", "Occupation", "Date of Birth", "Date Created").Freeze();
// Add customer details rows
excelTable.Rows.Add("1", "cfgewdfcrweg gfgfgfg", "Not Specified", "Client", "sdfsddffsd@yopmail.com", "", "Wellyx-Core", "", "09-08-2023", "");
excelTable.Rows.Add("2", "hsn test", "Not Specified", "Member", "hsntest@gmail.com", "", "Wellyx-Core", "", "17-10-2022", "");
using (var d = ExcelBuilder.Datasets(excelTable).Build())
{
// Specify the file path where you want to save the Excel file
string filePath = "DataTableToExcel-2-Customer-Report.xlsx";
d.SaveAsFile(filePath);
}
The SpanToMaxRowCells method is a custom method or extension method that appears to be designed to simplify the process of spanning a row's content across all available cells in that row, which can be beneficial for creating aesthetically pleasing and organized Excel sheets.
Example #3:
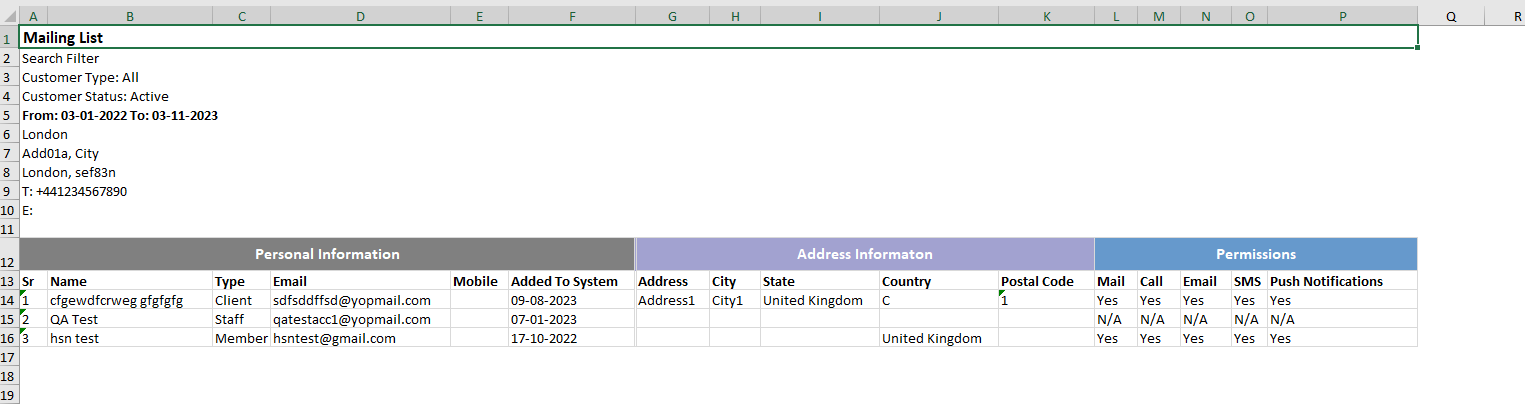
// Create two ExcelTable instances: excelTable1 and mailingReportDataTable
ExcelTable excelTable1 = new ExcelTable();
ExcelTable mailingReportDataTable = new ExcelTable();
// Link excelTable1 to mailingReportDataTable
excelTable1.Link(mailingReportDataTable);
// Add header and filter information to excelTable1
excelTable1.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false) { FontBold = true, FontSize = 13 }, "Mailing List").SpanToMaxRowCells();
excelTable1.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false), "Search Filter").SpanToMaxRowCells();
excelTable1.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false), "Customer Type: All").SpanToMaxRowCells();
excelTable1.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false), "Customer Status: Active").SpanToMaxRowCells();
excelTable1.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false) { FontBold = true }, "From: 03-01-2022 To: 03-11-2023").SpanToMaxRowCells();
excelTable1.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false), "London").SpanToMaxRowCells();
excelTable1.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false), "Add01a, City").SpanToMaxRowCells();
excelTable1.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false), "London, sef83n").SpanToMaxRowCells();
excelTable1.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false), "T: +441234567890").SpanToMaxRowCells();
excelTable1.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false), "E: ").SpanToMaxRowCells();
excelTable1.Rows.Add().SpanToMaxRowCells();
// Create a top row for mailingReportDataTable with multi-row header and distinct styling for different sections
var topRow = new ExcelRow(new RowStyle
{
FontBold = true,
TopBorder = XLBorderStyleValues.Double,
Height = 25,
AlignmentVertical = XLAlignmentVerticalValues.Center,
FontSize = 12
});
topRow.AddCell("Personal Information", new CellStyle
{
Colspan = 6,
AlignmentHorizontal = XLAlignmentHorizontalValues.Center,
BackroundColor = XLColor.Gray,
FontColor = XLColor.White,
});
topRow.AddCell("Address Information", new CellStyle
{
AlignmentHorizontal = XLAlignmentHorizontalValues.Center,
BackroundColor = XLColor.BlueBell,
FontColor = XLColor.White,
Colspan = 5
});
topRow.AddCell("Permissions", new CellStyle
{
AlignmentHorizontal = XLAlignmentHorizontalValues.Center,
BackroundColor = XLColor.BlueGray,
FontColor = XLColor.White,
Colspan = 5,
});
mailingReportDataTable.Rows.Add(topRow);
// Add column headers to mailingReportDataTable
mailingReportDataTable.Rows.Add(new RowStyle { FontBold = true, AlignmentVertical = XLAlignmentVerticalValues.Center }, "Branch", "Name", "Email", "Mobile", "Membership Created Date", "Membership", "Status", "Start Date", "End Date", "Roll Over", "Reason", "Notes", "Expired/Terminated Date");
// Add data rows to mailingReportDataTable
mailingReportDataTable.Rows.Add("Branch 1", "Babar Hassan", "babar@yopmail.com", "+442071773406", "13-03-2023 06:02 AM", "AppleDiscount33", "Terminated", "13-03-2023", "13-03-2273", "No", "Reason not given", "N/A", "26-09-2023 02:46 PM");
mailingReportDataTable.Rows.Add("Branch 1", "Sy Mehr", "sqmehr@yopmail.com", "+92 3345 045595", "26-04-2022 09:24 AM", "Crossfit Membership - Copy 2", "Terminated", "26-04-2022", "26-04-2023", "Yes", "Reason not given", "N/A", "15-03-2023 10:30 AM");
mailingReportDataTable.Rows.Add("Branch 1", "Babar Hassan", "babar@yopmail.com", "+442071773406", "13-03-2023 06:07 AM", "Crossfit Membership - 2", "Terminated", "13-03-2023", "13-03-2024", "Yes", "Reason not given", "N/A", "13-03-2023 06:53 AM");
mailingReportDataTable.Rows.Add("Branch 1", "Babar Hassan", "babar@yopmail.com", "+442071773406", "10-03-2023 01:30 PM", "WG - 12 Months x 4 $59.99", "Terminated", "10-03-2023", "06-04-2023", "Yes", "Reason not given", "N/A", "10-03-2023 01:32 PM");
mailingReportDataTable.Rows.Add("London", "shani 001", "shani66@yopmail.com", "N/A", "10-03-2023 10:25 AM", "interval", "Terminated", "10-03-2023", "10-03-2024", "No", "Reason not given", "N/A", "10-03-2023 12:15 PM");
mailingReportDataTable.Rows.Add("Branch 1", "Babar Hassan", "babar@yopmail.com", "+442071773406", "10-03-2023 11:53 AM", "Crossfit Membership", "Terminated", "10-03-2023", "10-03-2024", "Yes", "Reason not given", "N/A", "10-03-2023 11:59 AM");
mailingReportDataTable.Rows.Add("London Branch", "Ham Dard", "hamdard@yopmail.com", "N/A", "06-01-2023 11:28 AM", "12 month winter package - 1", "Terminated", "06-01-2023", "06-01-2024", "Yes", "Reason not given", "N/A", "06-01-2023 01:34 PM");
using (var d = ExcelBuilder.Datasets(excelTable1, mailingReportDataTable).Build())
{
var column = excelTableMailingReport.GetColumn("Personal Information");
excelTableMailingReport.GetColumn(column.EndColumnNumber).ColumnStyle.RightBorder = XLBorderStyleValues.Double;
// Specify the file path where you want to save the Excel file
string filePath = "DataTableToExcel-3-Mailing-List-Report.xlsx";
d.SaveAsFile(filePath);
}
// In this code snippet, two ExcelTable instances, `excelTable1` and `mailingReportDataTable`, are created.
// `excelTable1` is linked to `mailingReportDataTable`, establishing a connection between the two tables.
// The `excelTable1` is used to structure and organize information related to a "Mailing List."
// Various filter criteria, date ranges, and location details are added to enhance the context of the mailing list.
// The `mailingReportDataTable` is designed to display a detailed report with specific columns such as
// "Branch," "Name," "Email," "Mobile," and more. The top row of this table is customized to have a multi-row
// header with distinct styling for different sections like "Personal Information," "Address Information," and "Permissions."
// Subsequent rows in `mailingReportDataTable` contain data representing individual entries in the mailing list,
// including details like membership status, start and end dates, rollover information, reasons, and timestamps.
// Overall, this code snippet demonstrates the creation of structured Excel tables with linked tables,
// formatted headers, and organized data for a comprehensive and visually appealing mailing list report.
Example #4:
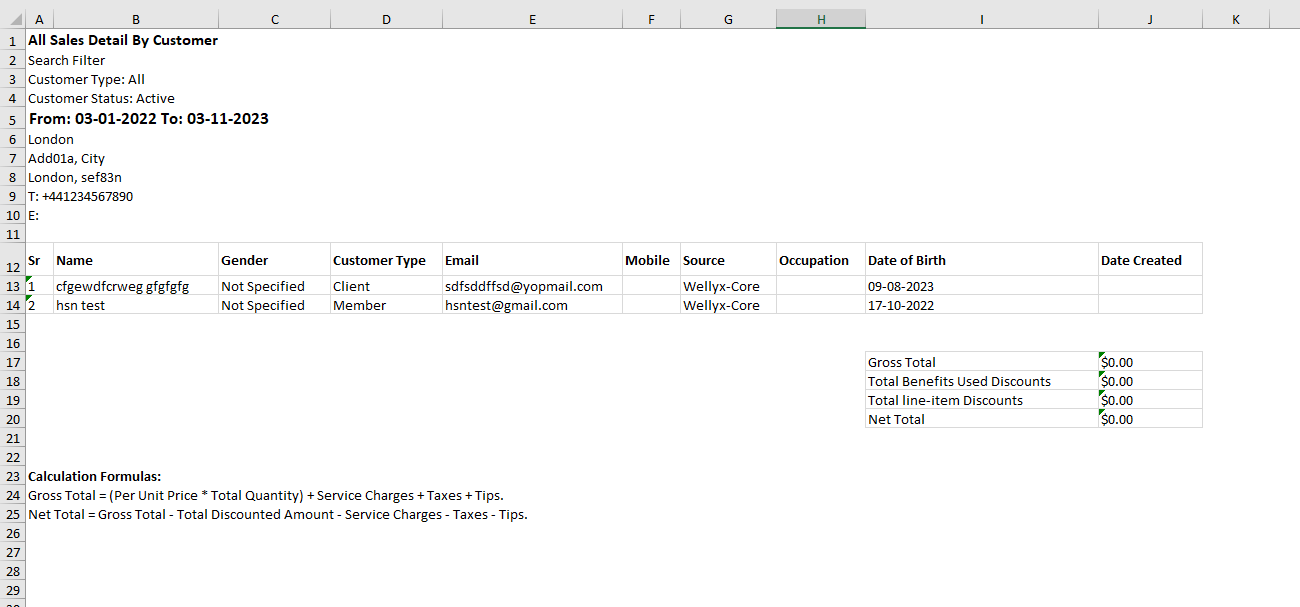
// Create ExcelTable instances: excelTable2, excelTable3, and excelTable4
ExcelTable excelTable2 = new ExcelTable();
ExcelTable excelTable3 = new ExcelTable();
ExcelTable excelTable4 = new ExcelTable();
// Add header and filter information to excelTable2
excelTable2.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false) { FontBold = true, FontSize = 12 }, "All Sales Detail By Customer").SpanToMaxRowCells();
excelTable2.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false), "Search Filter").SpanToMaxRowCells();
excelTable2.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false), "Customer Type: All").SpanToMaxRowCells();
excelTable2.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false), "Customer Status: Active").SpanToMaxRowCells();
excelTable2.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false) { FontBold = true, FontSize = 13 }, "From: 03-01-2022 To: 03-11-2023").SpanToMaxRowCells();
excelTable2.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false), "London").SpanToMaxRowCells();
excelTable2.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false), "Add01a, City").SpanToMaxRowCells();
excelTable2.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false), "London, sef83n").SpanToMaxRowCells();
excelTable2.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false), "T: +441234567890").SpanToMaxRowCells();
excelTable2.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false), "E: ").SpanToMaxRowCells();
excelTable2.Rows.Add().SpanToMaxRowCells();
// Add column headers and data rows to excelTable2
excelTable2.Rows.Add(new ExcelRow(new RowStyle
{
FontBold = true,
Height = 25,
AlignmentVertical = XLAlignmentVerticalValues.Center,
TopBorder = XLBorderStyleValues.Double
}, "Sr", "Name", "Gender", "Customer Type", "Email", "Mobile", "Source", "Occupation", "Date of Birth", "Date Created"));
excelTable2.Rows.Add(new ExcelRow("1", "cfgewdfcrweg gfgfgfg", "Not Specified", "Client", "sdfsddffsd@yopmail.com", "", "Wellyx-Core", "", "09-08-2023", ""));
excelTable2.Rows.Add(new ExcelRow("2", "hsn test", "Not Specified", "Member", "hsntest@gmail.com", "", "Wellyx-Core", "", "17-10-2022", ""));
// Add information to excelTable3
excelTable3.AlignTableEnd = true;
excelTable3.EmptyRowsBeforePresentation = 2;
excelTable3.Rows.Add("Gross Total", "$0.00");
excelTable3.Rows.Add("Total Benefits Used Discounts", "$0.00");
excelTable3.Rows.Add("Total line-item Discounts", "$0.00");
excelTable3.Rows.Add(new RowStyle { TopBorder = XLBorderStyleValues.Double }, "Net Total", "$0.00");
// Add information to excelTable4
excelTable4.EmptyRowsBeforePresentation = 2;
excelTable4.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false), new CellStyle { FontBold = true, Colspan = 4 }, "Calculation Formulas:");
excelTable4.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false), new CellStyle { Colspan = 6 }, "Gross Total = (Per Unit Price * Total Quantity) + Service Charges + Taxes + Tips.");
excelTable4.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false), new CellStyle { Colspan = 6 }, "Net Total = Gross Total - Total Discounted Amount - Service Charges - Taxes - Tips.");
using (var d = ExcelBuilder.Datasets(excelTable2, excelTable3, excelTable4).Build())
{
// Specify the file path where you want to save the Excel file
string filePath = "DataTableToExcel-4-All-Sales-Detail-By-Customer-Report.xlsx";
d.SaveAsFile(filePath);
}
// In this code snippet, an ExcelTable instance, `excelTable2`, is created to represent "All Sales Detail By Customer."
// The table is structured with various filter options, including customer type, status, and date range.
// The table's top section includes details like location, date range, and contact information. It also features
// a stylized header with distinct formatting for columns such as "Sr," "Name," "Gender," and more.
// Additionally, two linked ExcelTable instances, `excelTable3` and `excelTable4`, are created to display financial information.
// `excelTable3` represents gross and net totals, while `excelTable4` provides calculation formulas for better transparency.
// The overall structure of this code snippet showcases the creation of organized and visually appealing Excel tables
// with specific details on sales by customer, financial summaries, and calculation formulas.
Example #5:
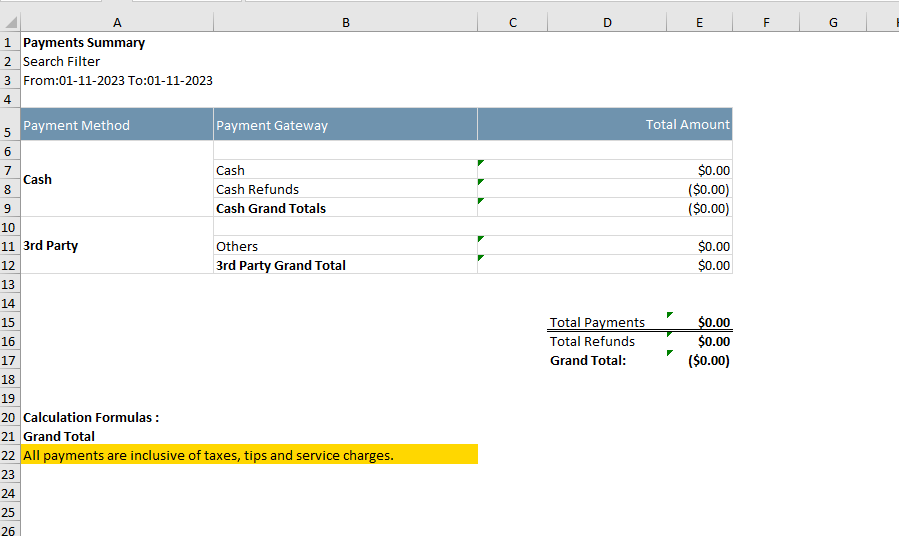
// Create an instance of ExcelTable for the payments summary
ExcelTable excelPaymentSummary = new ExcelTable();
excelPaymentSummary.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false) { FontBold = true }, "Payments Summary").SpanToMaxRowCells();
excelPaymentSummary.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false), "Search Filter").SpanToMaxRowCells();
excelPaymentSummary.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false), "From:01-11-2023 To:01-11-2023").SpanToMaxRowCells();
excelPaymentSummary.Rows.Add().SpanToMaxRowCells();
// Add a stylized header row for payment details
ExcelRow excelRow = new ExcelRow(new RowStyle { BackroundColor = XLColor.FromHtml("#6F93AE"), FontColor = XLColor.White, Height = 25, AlignmentVertical = XLAlignmentVerticalValues.Center });
excelRow.AddCell("Payment Method");
excelRow.AddCell("Payment Gateway");
excelRow.AddCell("Total Amount", new CellStyle { AlignmentHorizontal = XLAlignmentHorizontalValues.Right, Colspan = 3 });
excelPaymentSummary.Rows.Add(excelRow);
// Add rows for cash payments and refunds
ExcelRow excelRow1 = new ExcelRow();
excelRow1.AddCell("Cash", new CellStyle { Rowspan = 4, AlignmentVertical = XLAlignmentVerticalValues.Top, FontBold = true });
excelRow1.AddCell("", new CellStyle { Colspan = 4 });
excelPaymentSummary.Rows.Add(excelRow1);
ExcelRow excelRow2 = new ExcelRow();
excelRow2.AddCell();
excelRow2.AddCell("Cash");
excelRow2.AddCell("$0.00", new CellStyle { AlignmentHorizontal = XLAlignmentHorizontalValues.Right, Colspan = 3 });
excelPaymentSummary.Rows.Add(excelRow2);
ExcelRow excelRow3 = new ExcelRow();
excelRow3.AddCell();
excelRow3.AddCell("Cash Refunds");
excelRow3.AddCell("($0.00)", new CellStyle { AlignmentHorizontal = XLAlignmentHorizontalValues.Right, Colspan = 3 });
excelPaymentSummary.Rows.Add(excelRow3);
// Add a row for the grand total of cash payments
excelPaymentSummary.Rows.Add(new ExcelCell(), new ExcelCell("Cash Grand Totals", new CellStyle { FontBold = true }), new ExcelCell("($0.00)", new CellStyle { AlignmentHorizontal = XLAlignmentHorizontalValues.Right, Colspan = 3 }));
// Create another instance of ExcelTable for additional payment summary details
ExcelTable excelPaymentSummary1 = new ExcelTable();
excelPaymentSummary1.AlignTableEnd = true;
excelPaymentSummary1.EmptyRowsBeforePresentation = 2;
excelPaymentSummary1.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false), new ExcelCell("Total Payments"), new ExcelCell("$0.00", new CellStyle { AlignmentHorizontal = XLAlignmentHorizontalValues.Right, FontBold = true }));
excelPaymentSummary1.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false) { TopBorder = XLBorderStyleValues.Double }, new ExcelCell("Total Refunds"), new ExcelCell("$0.00", new CellStyle { AlignmentHorizontal = XLAlignmentHorizontalValues.Right, FontBold = true }));
excelPaymentSummary1.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false) { FontBold = true }, new ExcelCell("Grand Total:"), new ExcelCell("($0.00)", new CellStyle { AlignmentHorizontal = XLAlignmentHorizontalValues.Right, FontBold = true }));
// Create another instance of ExcelTable for additional payment summary details
ExcelTable excelPaymentSummary2 = new ExcelTable();
excelPaymentSummary2.EmptyRowsBeforePresentation = 2;
excelPaymentSummary2.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false), new ExcelCell("Calculation Formulas :", new CellStyle() { Colspan = 2, FontBold = true }));
// Add rows to excelPaymentSummary2 explaining the calculation formulas
var excelRichCell = new ExcelCell(new CellStyle() { Colspan = 2 });
excelRichCell.RichText.Add(new RichTextValue { Value = "Grand Total", Bold = true });
excelRichCell.RichText.AddALine(new RichTextValue { Value = " = Total Payments - Total Refunds" });
excelPaymentSummary2.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false), excelRichCell);
excelPaymentSummary2.Rows.Add(new RowStyle(false), new ExcelCell("All payments are inclusive of taxes, tips and service charges.", new CellStyle() { Colspan = 2, BackroundColor = XLColor.FromHtml("#FFD700") }));
//Save the Excel package to a file
using (var d = ExcelBuilder.Datasets(excelPaymentSummary, excelPaymentSummary1, excelPaymentSummary2).Build())
{
// Specify the file path where you want to save the Excel file
string filePath = "DataTableToExcel-5-Payment-Summary.xlsx";
d.SaveAsFile(filePath);
}
// In this code snippet, three ExcelTable instances, `excelPaymentSummary`, `excelPaymentSummary1`, and `excelPaymentSummary2`, are created.
// `excelPaymentSummary` is designed to provide a summary of payments, including details like payment method, gateway, and total amounts.
// The table includes stylized headers and rows, with specific formatting for cash payments and refunds.
// `excelPaymentSummary1` displays a concise summary of total payments, refunds, and the grand total, featuring proper formatting and borders.
// `excelPaymentSummary2` includes information about calculation formulas, clarifying the calculation of the grand total as the difference between total payments and total refunds.
// The code demonstrates the creation of detailed and organized Excel tables, presenting payment summaries with clear formatting and calculated totals.
Example #6
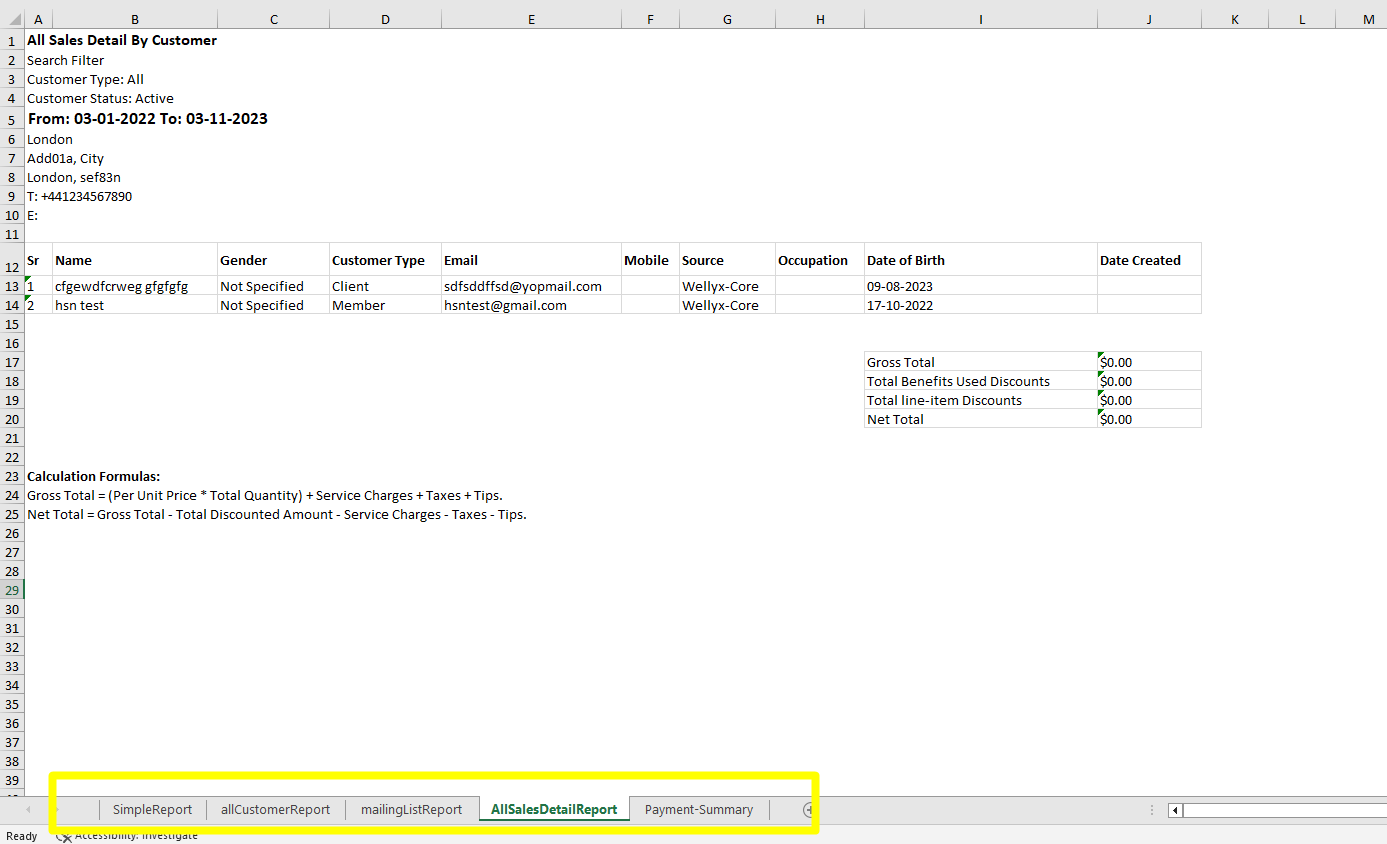
Creating composite/with multiple Excel Sheet
using (var d = ExcelBuilder.Datasets(new Worksheet("SimpleReport", simpleexcelTable), new Worksheet("allCustomerReport", excelTable), new Worksheet("mailingListReport", mailingReportDataTable), new Worksheet("AllSalesDetailReport", excelTable2, excelTable3, excelTable4), new Worksheet("Payment-Summary", excelPaymentSummary, excelPaymentSummary1, excelPaymentSummary2)).Build())
{
// Specify the file path where you want to save the Excel file
string filePath = "composit-report.xlsx";
excelPaymentSummary1.GetColumn("column1").ColumnStyle.BackroundColor = XLColor.Blue;
d.SaveAsFile(filePath);
}